In order to effectuate successful and meaningful collaborative learning, the teams should function well. This does not differ for collaborative learning that (mainly or only) uses online tools. As a teacher -and consequently as a coach, supervisor and the one with final responsibility for this collaborative learning- you have an interest in having sufficient insight in the following group dynamics;
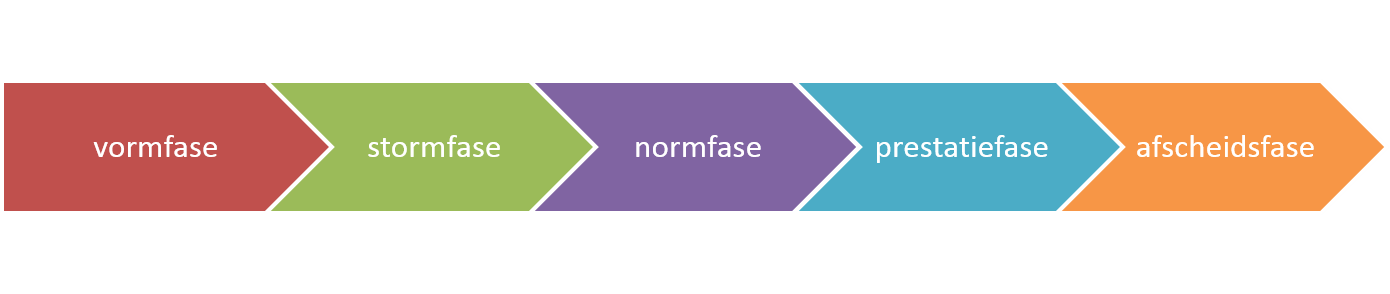
- According to Tuckman five stages can be distinguished in the developments of teams. These are, in order of occurance: forming – storming – norming – performing and adjourning (also called ‘mourning’) stage.
According to Tuckman, a team undergoes these stages in a chronological order and a team can never perform well if they have not had conflicts together (storming phase) and have not made arrangements (forming).
In the meantime, it is noted that the different stages do not always need to be traversed one after the other. . On the contrary, a lot of teams are stuck in the middle. They develop rules of conduct and arrangements that are counterproductive.
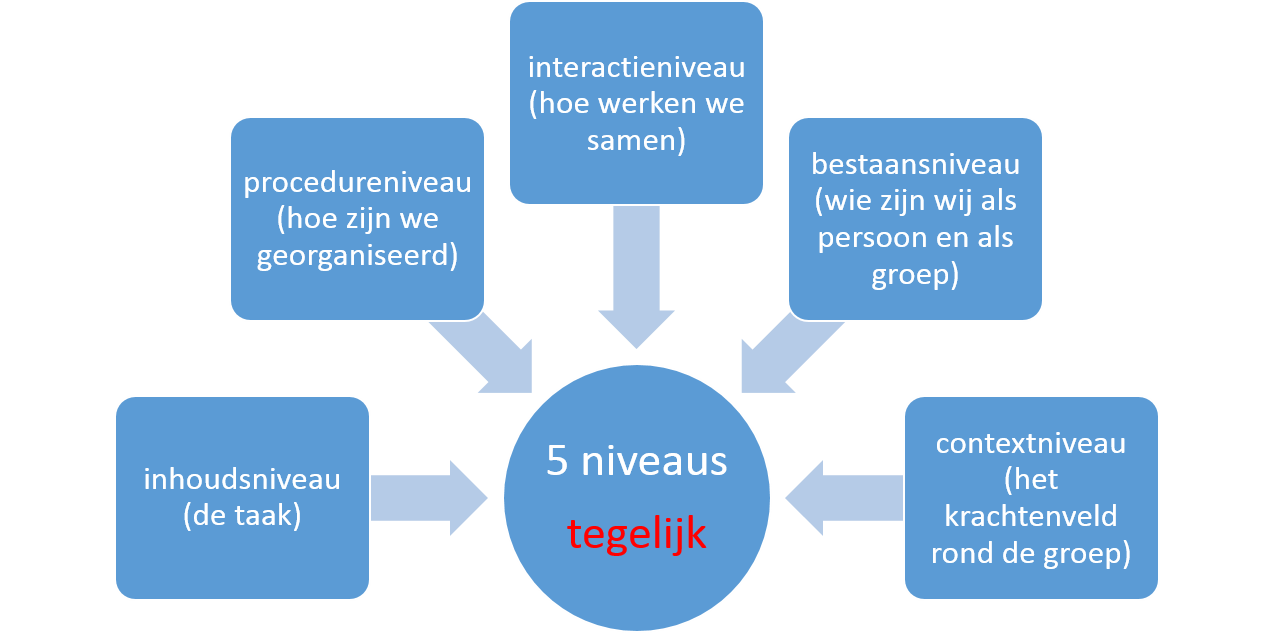
- Collaborating in groups can be better understood if you are aware of the fact that this happens at five levels at the same time. The content level (the task) is one of them. Next to that, there is a procedure level (how are we organized), an interaction level (how are we working together), a subsistence level (who are we as individuals and as a group) and a context level (the field of forces around the group).
Two important observations result from this model. A first one is that you are often see that problems and conflicts are being fought on a different level than the level at which the problem is situated. A disagreement over “who is right?” is to be situated at the procedure level (e.g. if in the underlying discussion is about ‘who chose the right approach’) or at the subsistence level (e.g. who should get all the credit). Secondly, you can notice that a prerequisite for a good collaboration is that a team should be able to switch from one level to another. Distorted teamwork arises when there is a blockage at some level (e.g. the procedural rules are unassailable) or in case of a shift (when one conflict is transferred to a conflict at another level that is off-limits)
Tip: in case of bigger group projects, it can be interesting to share these insights with you students before the start of the project.
LINKS
Want to start right away?
Want to know more about…